Hand Muscles Anatomy Biology Diagrams The skeletal muscles of the hand are responsible for the movement of the hand and fingers.[1] These muscles subdivide into two groups: the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles.[2][3] The extrinsic muscle group is called so because the muscle belly originates in the forearm.[2][4] The intrinsic muscle groups consist of smaller muscles solely located within the various hand osseofascial compartments

Learn about the hand muscles, their attachment, nerve supply and action. The hand muscles are divided into extrinsic and intrinsic groups, and include thenar, hypothenar, lumbrical and interossei muscles.
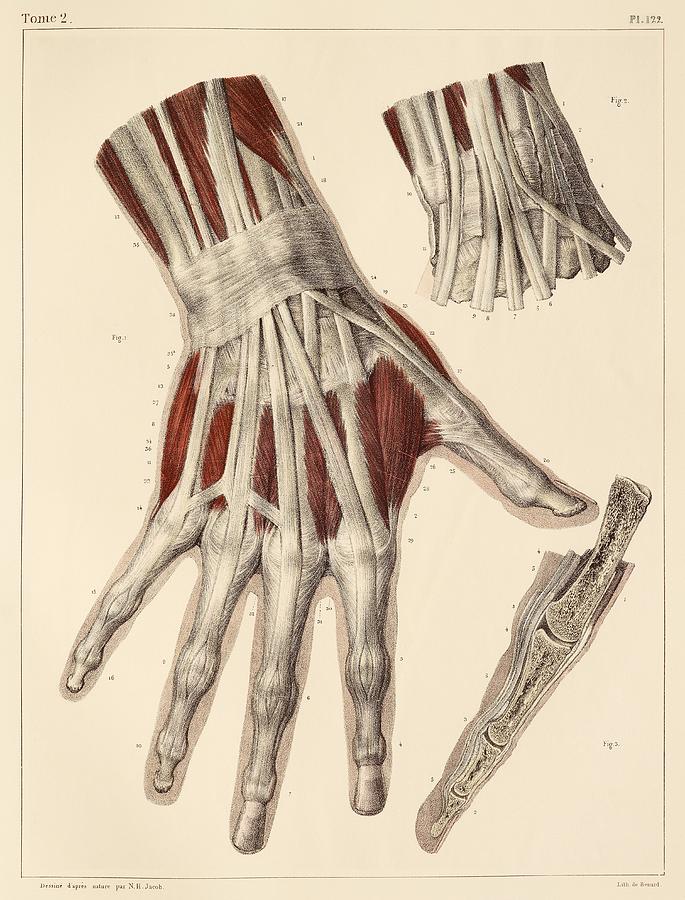
The Muscles of the Hand: Anatomy and 3D Illustrations Biology Diagrams
Learn about the 11 intrinsic and 15 extrinsic muscles in each hand that help with thumb, finger, and palm movements. See the muscle origin, insertion, action, and innervation for each muscle group.

Learn about the structure and function of your hand and wrist, including the 19 bones, 34 muscles, nerves, tendons and ligaments that make them work. Find out how to care for your hand and wrist health and what conditions can affect them. Learn about the bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, and nerves of the human hand, an extraordinary part of the upper limb. See detailed diagrams and descriptions of the hand's anatomy and how it works. Learn about the anatomy and function of the muscles of the hand, which are divided into extrinsic and intrinsic groups. The extrinsic muscles are located on the forearm and the intrinsic muscles are located within the hand itself.

Hand Anatomy: Bones & Muscles Full Review Biology Diagrams
Learn about the structure and function of the hand, the most distal part of the upper limb. Explore the carpal, metacarpal and phalangeal bones, the thenar, hypothenar and lumbrical muscles, and the median, ulnar and radial nerves and arteries.
